Deno Deploy is a distributed system that runs javascript, typescript and webassembly at the edge, worldwide. You don't need to deal with infrastructure at all, but instead just upload your code and you are done. QStash is a message-queue/scheduler with the same benefits, because it is 100% serverless and offers per-request pricing.
Together they can be used to build failure-tolerant asynchronous processing in serverless functions with minimal setup.
Let's take a look on how to use QStash together with Deno. To highlight the simplicity, we will do everything within the code editor at dash.deno.com
1. Create a new project
Go to dash.deno.com/new and create a new playground
project by clicking on Play 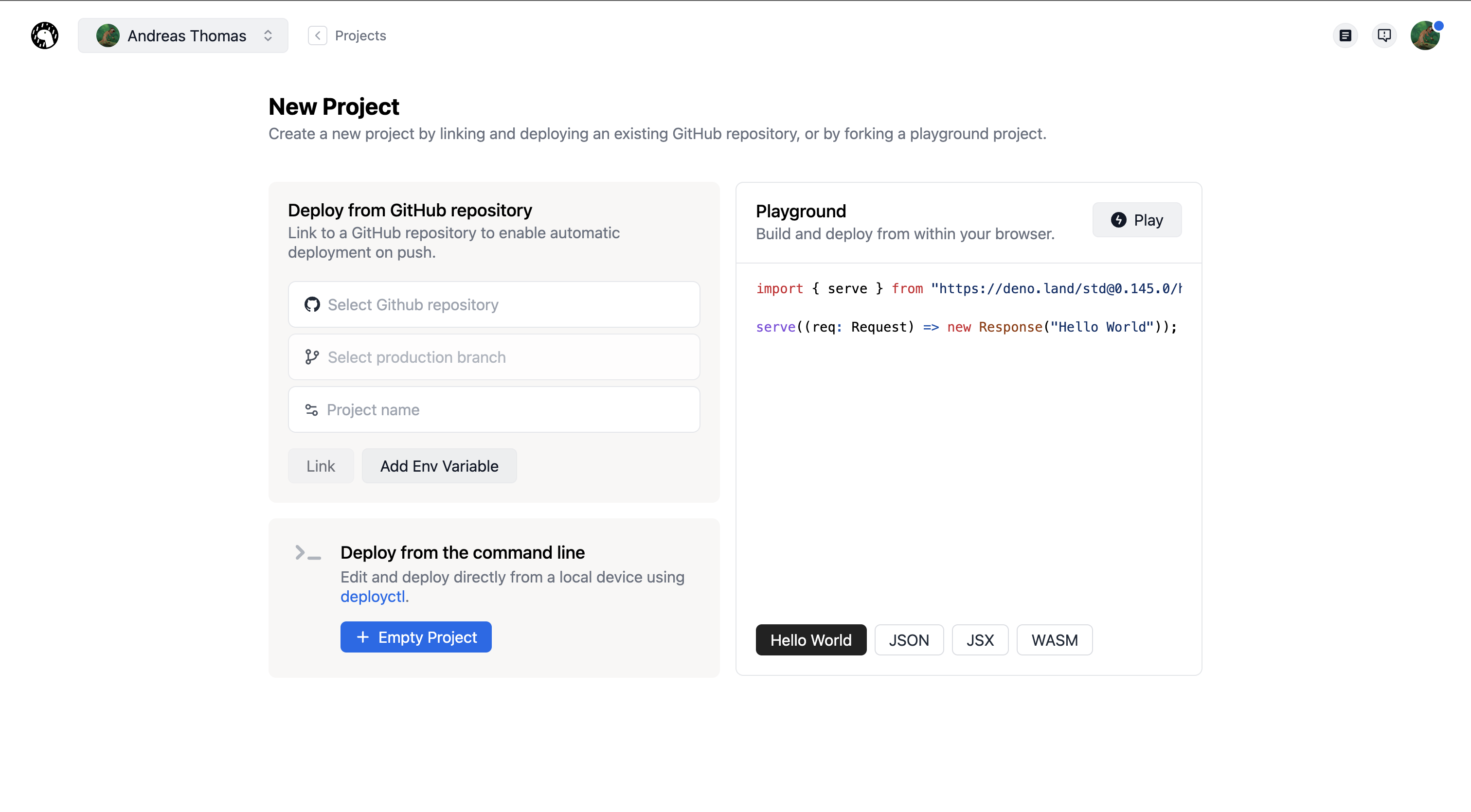
2. Edit the handler function
QStash uses HTTP requests to push messages to your API, we offer a simple
utility to verify the authenticity of each incoming request. Just import the
Receiver class and create a new instance with your secret signing keys.
Replace the existing code with the following:
import { serve } from "https://deno.land/std@0.142.0/http/server.ts";
import { Receiver } from "https://deno.land/x/upstash_qstash@v0.1.4/mod.ts";
serve(async (req: Request) => {
const r = new Receiver({
currentSigningKey: Deno.env.get("QSTASH_CURRENT_SIGNING_KEY")!,
nextSigningKey: Deno.env.get("QSTASH_NEXT_SIGNING_KEY")!,
});
const body = await req.text();
const isValid = await r
.verify({
signature: req.headers.get("Upstash-Signature")!,
body,
})
.catch((err: Error) => {
console.error(err);
return false;
});
if (!isValid) {
return new Response("Invalid signature", { status: 401 });
}
// At this point the request is valid and you can start processing the message
console.log(body);
return new Response("OK", { status: 200 });
});import { serve } from "https://deno.land/std@0.142.0/http/server.ts";
import { Receiver } from "https://deno.land/x/upstash_qstash@v0.1.4/mod.ts";
serve(async (req: Request) => {
const r = new Receiver({
currentSigningKey: Deno.env.get("QSTASH_CURRENT_SIGNING_KEY")!,
nextSigningKey: Deno.env.get("QSTASH_NEXT_SIGNING_KEY")!,
});
const body = await req.text();
const isValid = await r
.verify({
signature: req.headers.get("Upstash-Signature")!,
body,
})
.catch((err: Error) => {
console.error(err);
return false;
});
if (!isValid) {
return new Response("Invalid signature", { status: 401 });
}
// At this point the request is valid and you can start processing the message
console.log(body);
return new Response("OK", { status: 200 });
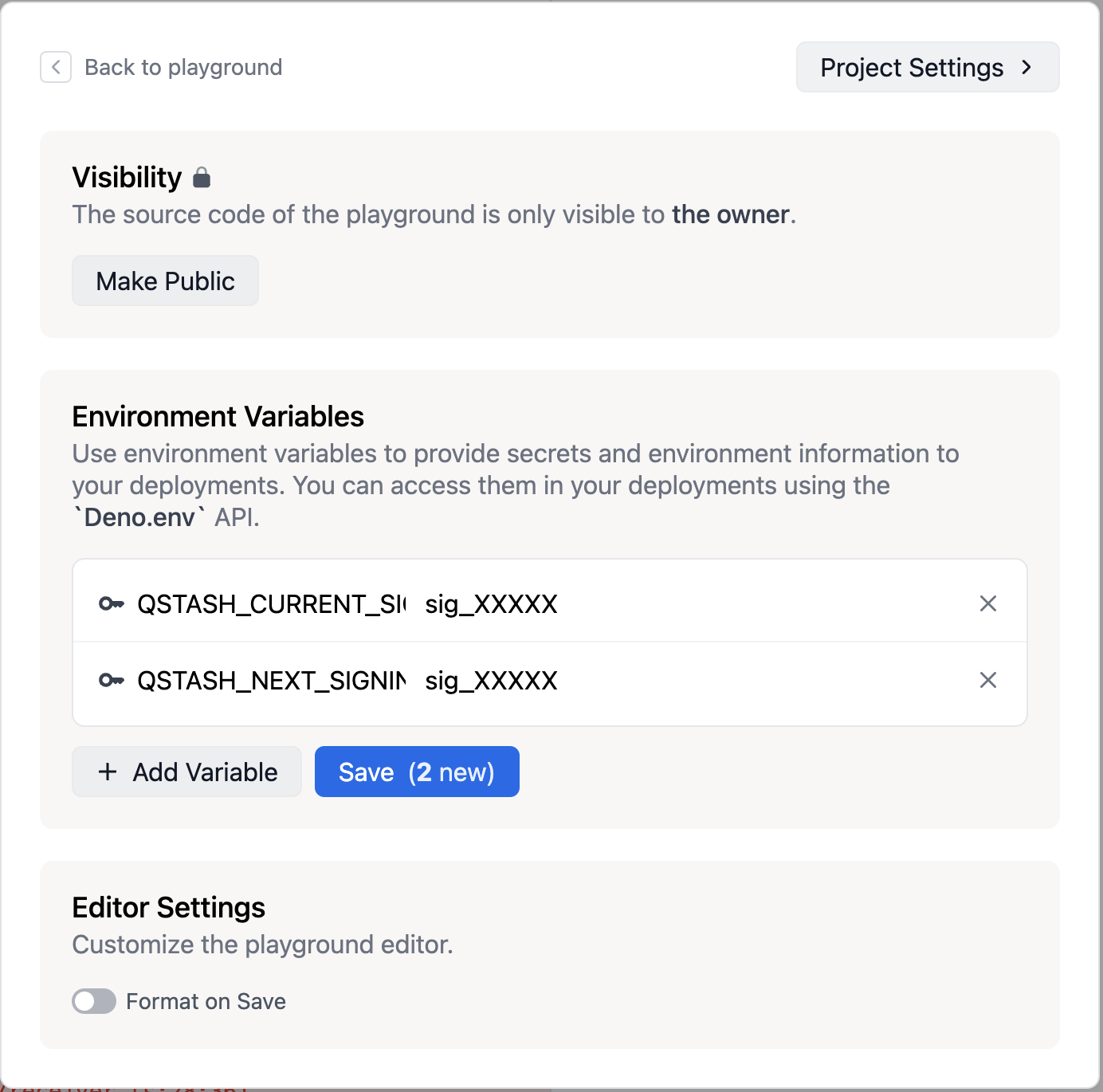
});3. Add your signing keys
Click on the settings button at the top of the screen and then click + Add Variable
Get your QSTASH_CURRENT_SIGNING_KEY and QSTASH_NEXT_SIGNING_KEY from
Upstash and then set them in deno deploy.
4. Deploy
Simply click on Save & Deploy at the top of the screen.
5. Publish a message
Make note of the url displayed in the top right. This is the public url of your project.
curl --request POST "https://qstash.upstash.io/v1/publish/https://early-frog-33.deno.dev" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <QSTASH_TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{ \"hello\": \"world\"}"curl --request POST "https://qstash.upstash.io/v1/publish/https://early-frog-33.deno.dev" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <QSTASH_TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{ \"hello\": \"world\"}"In the logs below the code editor you should see something like this:
Listening on http://localhost:8000/
{"hello": "world"}Listening on http://localhost:8000/
{"hello": "world"}Next Steps
That's it, you have successfully created a secure deno API, that receives and verifies incoming webhooks from qstash.
Learn more about publishing a message to qstash here
